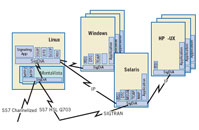
Dialogic
Signaling W/S
Dialogic® Distributed Signaling Interface (DSI) supports a wide range of Signaling System 7 (SS7) and internet protocol capabilities to manage the signaling traffic between an application and the SS7 network over TDM or IP. Together the Dialogic® DSI Network Interface Boards, DSI Protocol Libraries, and DSI Signaling Servers enable equipment manufacturers and developers to create cost-effective, scalable solutions for today’s modular networks. DSI components are linked into a run-time environment that coordinates the execution of signaling operations among separate processors in the configuration: the application host computer, the SS7 interface board with protocol acceleration capabilities, and remote signaling servers where messages can be processed without use of host computer cycles. The DSI message handling software transports signaling information between protocol layers or between a protocol layer and an application layer in a totally transparent way, regardless of the physical source and destination of the messages.DSI products deliver numerous benefits including:- Flexibility to meet diverse requirements worldwide with a mix of the best platforms and most suitable form factors for excellent price-performance and rapid time to market
- Development investment protection through portability of the same applications from boards, to servers, to SS7 over IP (SIGTRAN)
- Proven track record of deployment for more than a decade
- Signal message monitoring on TDM and IP to enable distinctive service delivery and enhanced security
Signaling W/S Signaling Serer & Gateway Signaling Boards
Software |
O/S |
Description |
Linux |
Delivers high-performance, high-density protocol monitoring that enables applications to interrogate SIGTRAN traffic between active signaling points and trigger intelligent actions. SIGTRAN Monitor, a software only application, joins Dialogic® Network Interface Boards that have circuit-switched network monitoring capabilities. |
|
Linux |
(Message Transfer Part) as defined by the ITU-T, ANSI. |
|
Linux |
(Signaling Connection Control Part class 0,1,2) ITU-T recommendations Q.711-Q.714, Q.791 and ANSI T1.112 |
|
Linux |
(Transaction Capabilities Application Part) ITU-T Q.771-Q.774 and ANSI T1.114 |
|
Linux |
(Mobile Application Part) GSM TS 09.02, TS 29.002 |
|
Linux |
CAMEL Application Part specifications v1-v3 |
|
Linux |
(Intelligent Networking) ITU CS1, ETSI CS1 & CS2 and GR-1299-CORE AIN |
|
Linux |
ANSI/TIA/EIA-41.5-D, Wireless Intelligent Networking (WIN) extensions ANSI/TIA/EIA-751, ANSI/TIA/EIA-764, ANSI/TIA/EIA-771, ANSI/TIA/EIA-826 [Prepaid] |
|
Linux |
(ISDN User Part) ITU-T Q.761-Q.764, Q.767, ETS 300 356-1, ANSI T1.113, national variants including German ISUP, Japanese TTC ISUP. |
|
Linux |
(MTP3 User Adaptation Layer ASP and IPSP) IETF RFC 3332 |
|
Linux |
SUA (Signaling Connection Control Part User Adaptation) RFC 3868 |
|
Linux |
(Bearer Independent Call Control) Q.1902.1 ? Q1902.5, Q.765.5, Signalling Transport Converter Q.1901 |
|
Linux |
(Telephony User Part) Q.721 - Q.725, French SSUTR2, Chinese GF001-9001 |
|
Linux |
(Stream Control Transmission Protocol) IETF RFC2960, RFC3309 |
|
Linux |
(MTP2 User Peer-to-Peer Adaptation Layer) IETF M2PA |